Configuration overview: Browser-based zero trust access using SSH or RDP
To allow clientless browser-based Zero Trust Access to private resources using SSH or RDP:
- If you are using older SSH servers, see Details: Supported options for SSH.
- Configure your private resource:
- Allow access using the applicable protocol for the internally reachable address. See
Add a Private Resource.
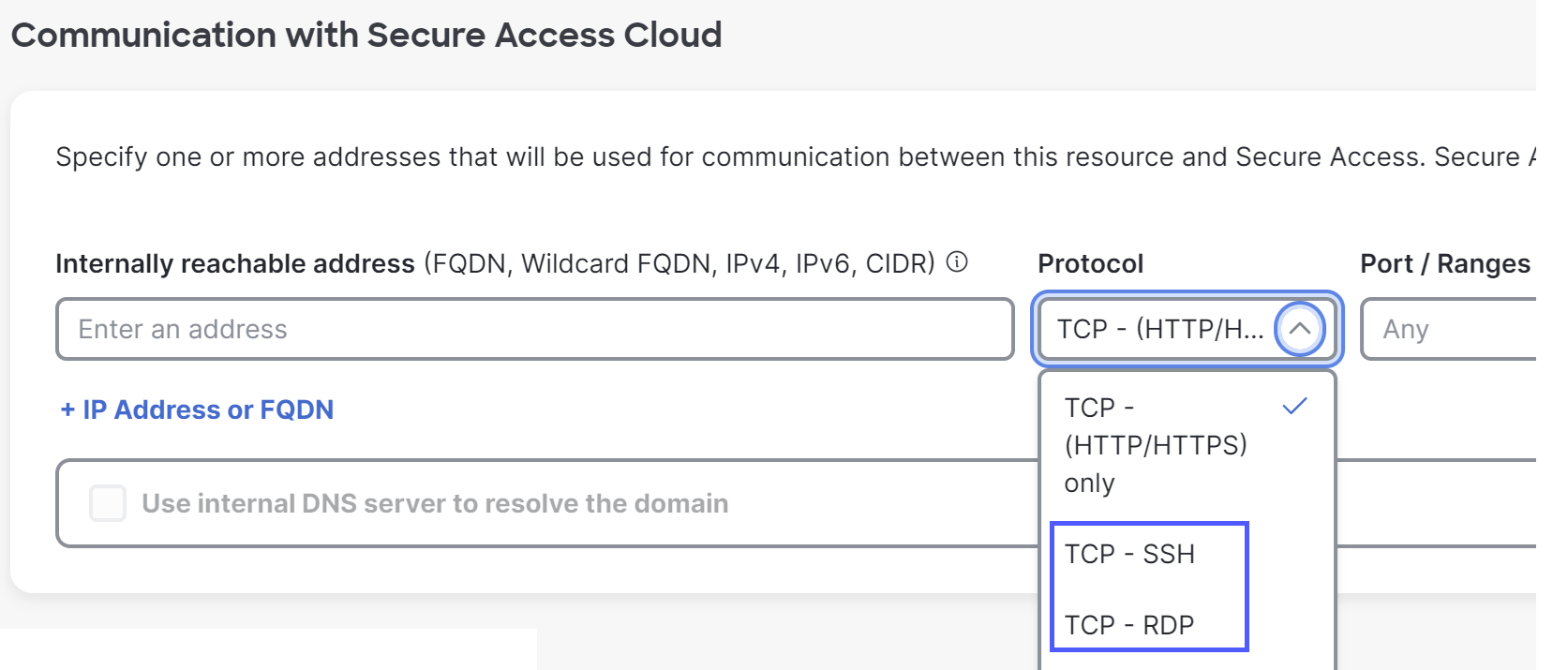
The resource name will appear at the top of your users' SSH or RDP window. - Allow access using the applicable protocol for the internally reachable address. See
Add a Private Resource.
- In the Private Resource, enable Zero-trust connections, then enable and configure browser-based connections.
- Follow the instructions for granting access to private destinations in Get Started With Private Access Rules.
- If your environment has a web proxy or firewall between end user browsers and the Secure Access cloud, you must allow websocket access on port 443 from your users' browsers to Secure Access.
- When you give users the applicable SSH or RDP credentials or private key for the resource, also provide the public URL for browser-based Zero Trust Access that you configured on the Private Resource page. Neither Secure Access nor the browser stores the credentials or private key.

