Policies Based on Service Name
Use the following information to verify and troubleshoot policies based on Service name on Windows OS workloads.
The following sections describe the way that the policies should appear on the workload.
Sample Policy Based on Service Name
dst_ports {
start_port: 22
end_port: 22
provider_filters {
service_name: “sshd”
}
}}
ip_protocol: TCP
address_family: IPv4
inspection_point: INGRESS
Generated Firewall Rule
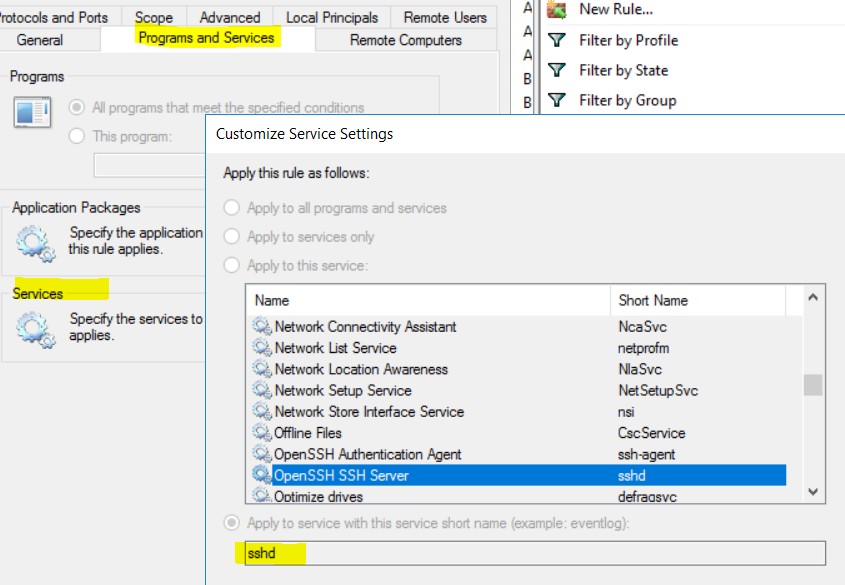
Generated Filter Using netsh
To verify using native Windows tools, that a filter has been added for an advanced policy:
-
With administrative privileges, run
cmd.exe. -
Run
netsh wfp show filters. -
The output file, filters.xml, is generated in the current directory.
-
Check FWPM_CONDITION_ALE_USER_ID for user name in the output file: filters.xml.
<item> <fieldKey>FWPM_CONDITION_ALE_USER_ID</fieldKey> <matchType>FWP_MATCH_EQUAL</matchType> <conditionValue> <type>FWP_SECURITY_DESCRIPTOR_TYPE</type> <sd>O:SYG:SYD:(A;;CCRC;;;S-1-5-80-3847866527-469524349-687026318- →516638107)</sd> </conditionValue> </item>
Generated WFP Filter Using tetenf.exe -l -f
Filter Name: Secure Workload Rule 3
------------------------------------------------------
EffectiveWeight: 18446744073709551590
LayerKey: FWPM_LAYER_ALE_AUTH_RECV_ACCEPT_V4
Action: Permit
Local Port: 22
Protocol: 6
User or Service: NT SERVICE\sshd
Invalid Service Name
-
In WAF mode, the Firewall rule is created for a nonexistent service name.
-
In WFP mode, the WFP filter is not created for a nonexistent service name.
-
Service SID type must be Unrestricted or Restricted. If the service type is None, the Firewall Rule and WFP filter can be added but they have no effect.
To verify the SID type, run the following command:
sc qsidtype <service name>
