Steps to perform scope suggestion
To invoke scope suggestion for a desired scope user should locate on the scopes page and select it.
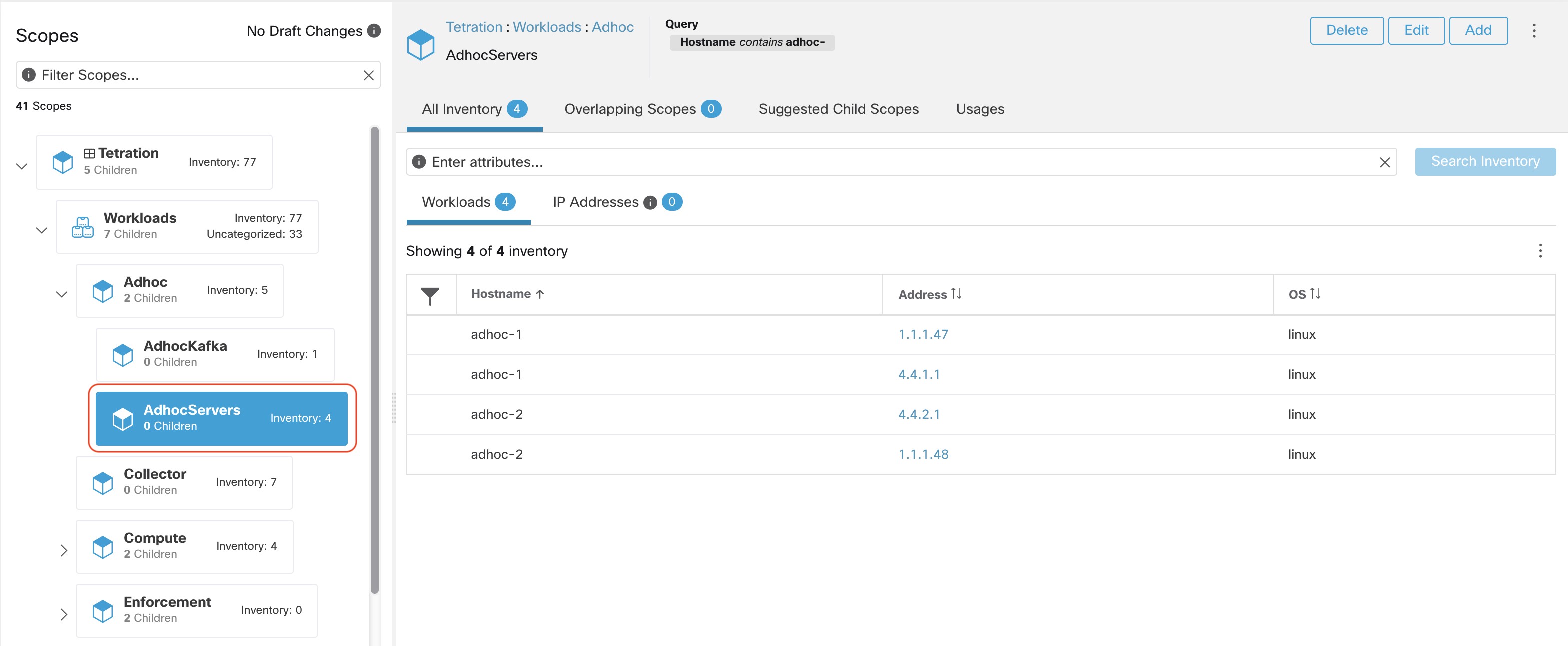
In the window, user can browse the inventory, uncategorized inventory items, i.e. those items that belong to the current selected scope and that do not belong to any of the current selected scope’s child scopes. Clicking on the uncategorized inventory items allows one to view this list.
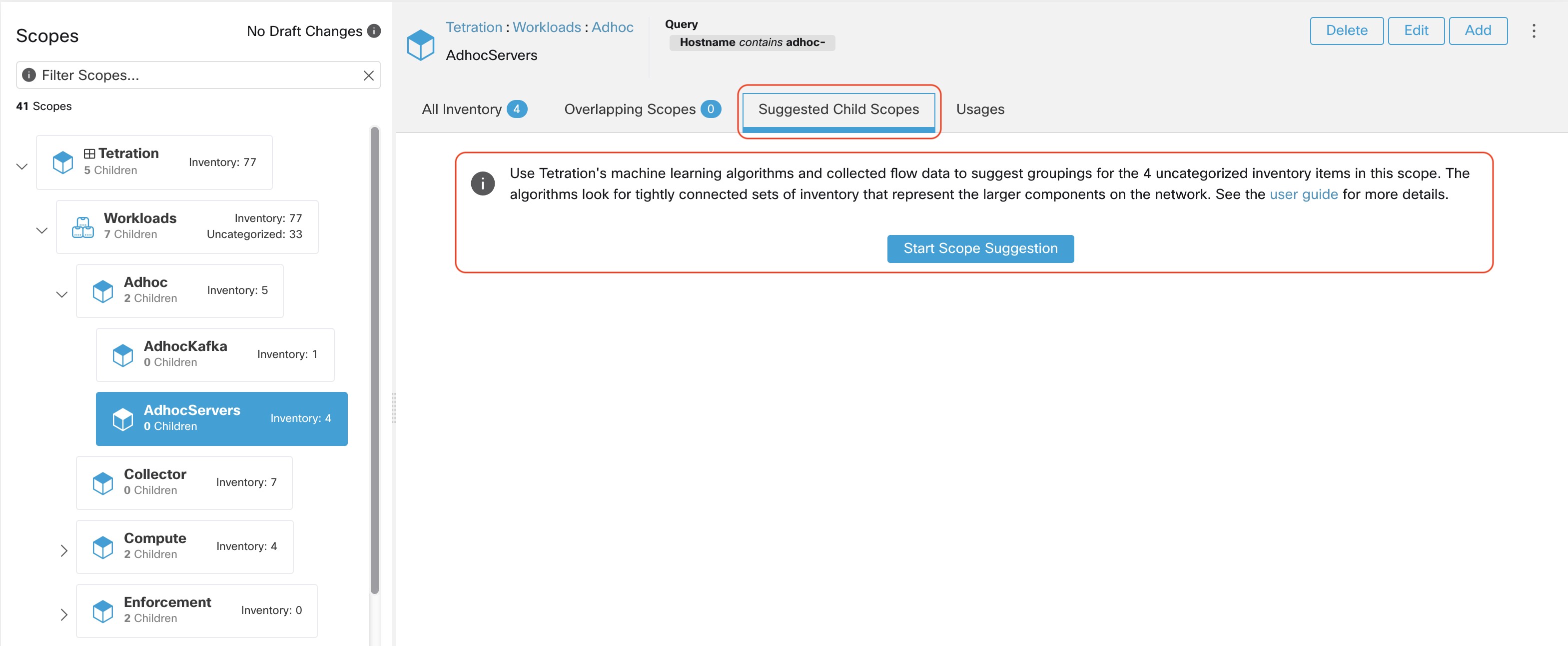
After selecting the scope user can click on Suggest Child Scopes, and click on Start Scope Suggestion (or click on Rerun, in case this is not the first time). Note that the input for a scope suggestion run will be the uncategorized inventory items.
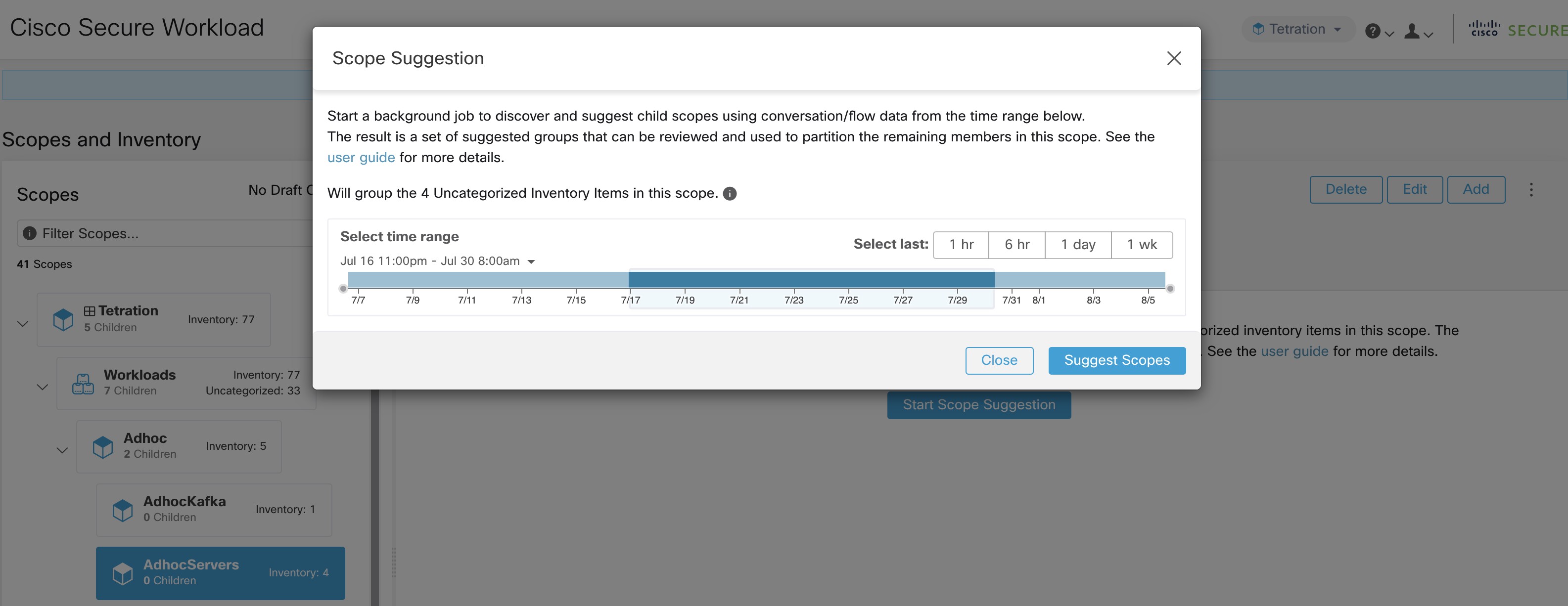
User can set the date range as input for scope suggestion and click on Suggest Scopes. A scope suggestion run is often fast under medium overall load, and takes only a few minutes for processing ten to thousands of endpoints, with tens of thousands of conversations.
The output is shown to the user as a list of candidates, currently up to 20 groups (shown), each accompanied with information such as group confidence (quality), a candidate scope name, and queries. Each discovered group has an associated Group Community Confidence, the possible values being: Very High, High, Medium and Low. This is a measure of the Community property of the group: the higher the confidence, the higher the community property of the given group of endpoints (many edges inside the group, relatively few edges to outside). Currently, the subset of groups picked to be shown are selected based on the Group Community Confidence. The groups discovered can currently fall under one of these four group types:
-
Generic Group: Any group discovered via machine learning based on the community property. Note that any group that is not explicitly designated with the special types below is a generic group.
-
Common Service: This group consists of endpoints that communicate with much of the input inventory. These endpoints could be running some kind of shared service(s).
-
Common Service Clients: This group consists of endpoints that only communicate with the Common Service group.
-
Ungrouped: This group consists of endpoints that cannot be grouped since they don’t have sufficient commu- nications.
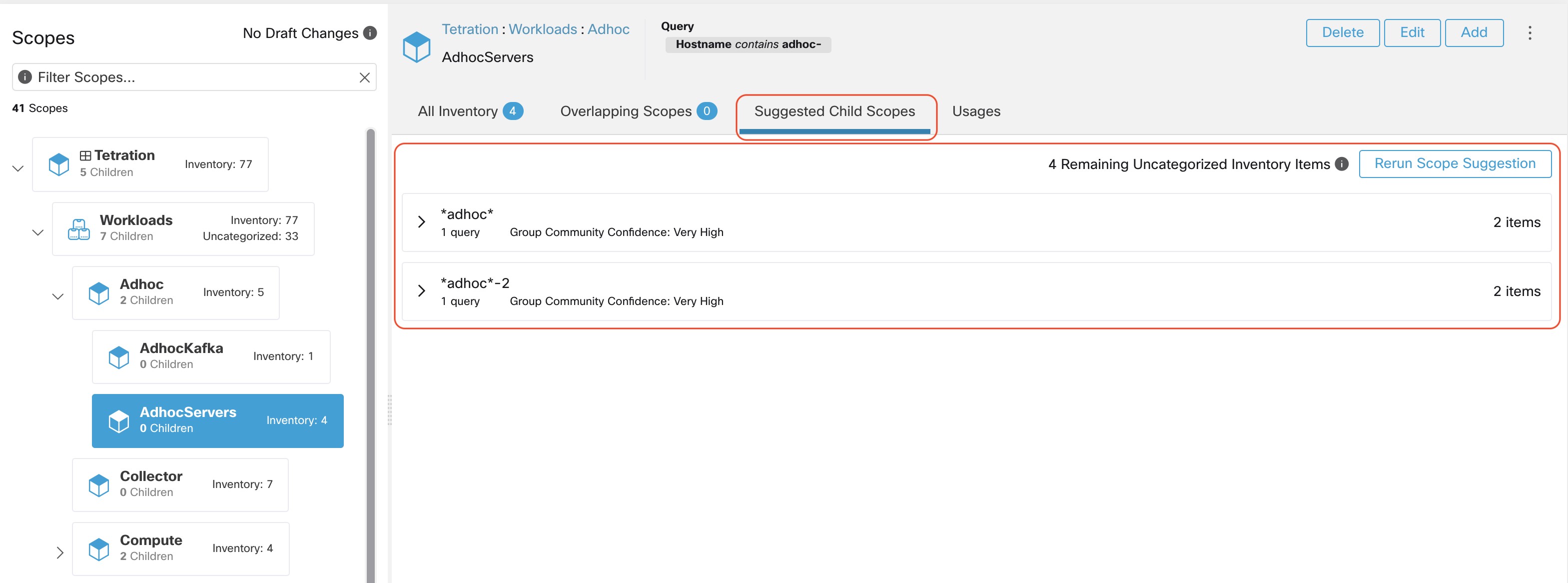
The user can click on a discovered group to view the list of queries generated for the selected group. The user can preview the inventory covered by the query which will closely define the discovered group. The queries consist of IP-ranges, subnets, host names and user uploaded labels. There is a confidence measure associated with each group called Query confidence which can have one of the following range of values Perfect, Very High, High, Medium and Low. For query generation, first the groups are discovered via graph processing and machine learning, then the queries are generated for each group. Query Confidence is a measure of how well the query can cover the endpoints. A query confidence of Perfect indicates that the query exactly covers the suggested (discovered) group. On the other end of the spectrum, a Low query confidence indicates that the query significantly misses out on exactly capturing the suggested group, which means that the query covers many Extra IPs (not part of the discovered group) and/or has many Missing IPs (not covered by the query).
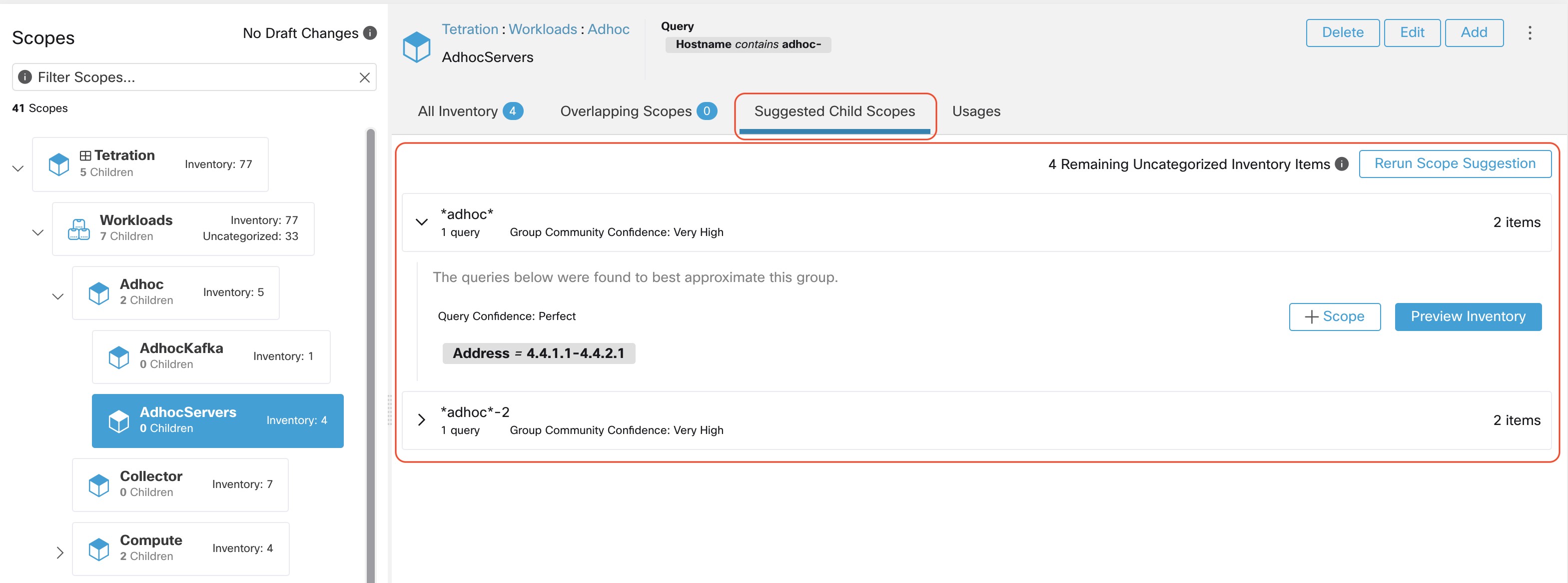
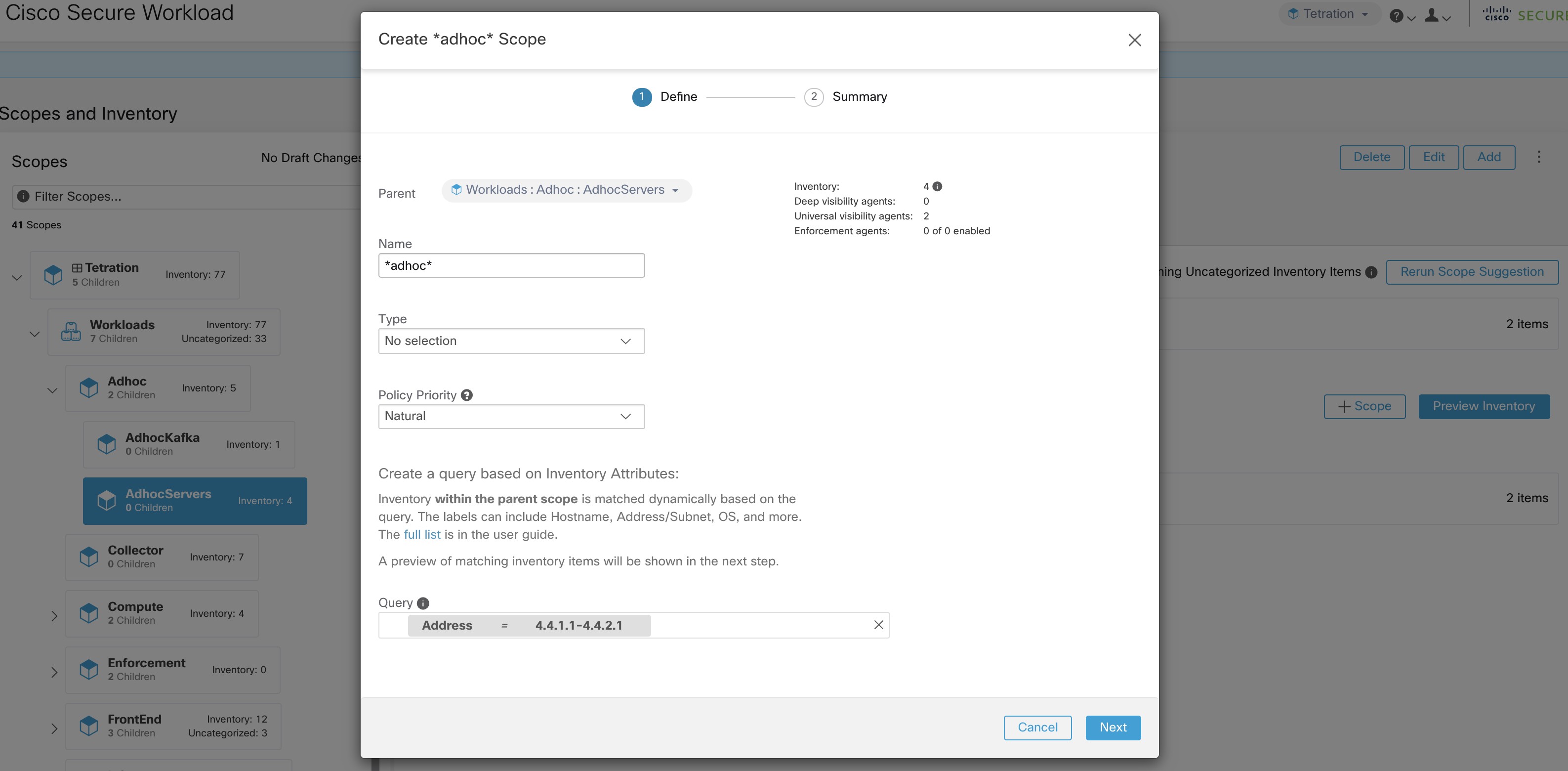
The user can click on + Scope button which will take the user to an edit window where the user can edit the group name and group query. The user can examine a query, the IPs that it matches, and decide whether some IPs need to be added or removed by adjusting the query. Once satisfied, the user can then click on Next, to review and convert the group to a scope on the draft view canvas.
After the user has converted a suggested group to a scope, the group slot turns green and the Uncategorized Inventory Items count decreases.
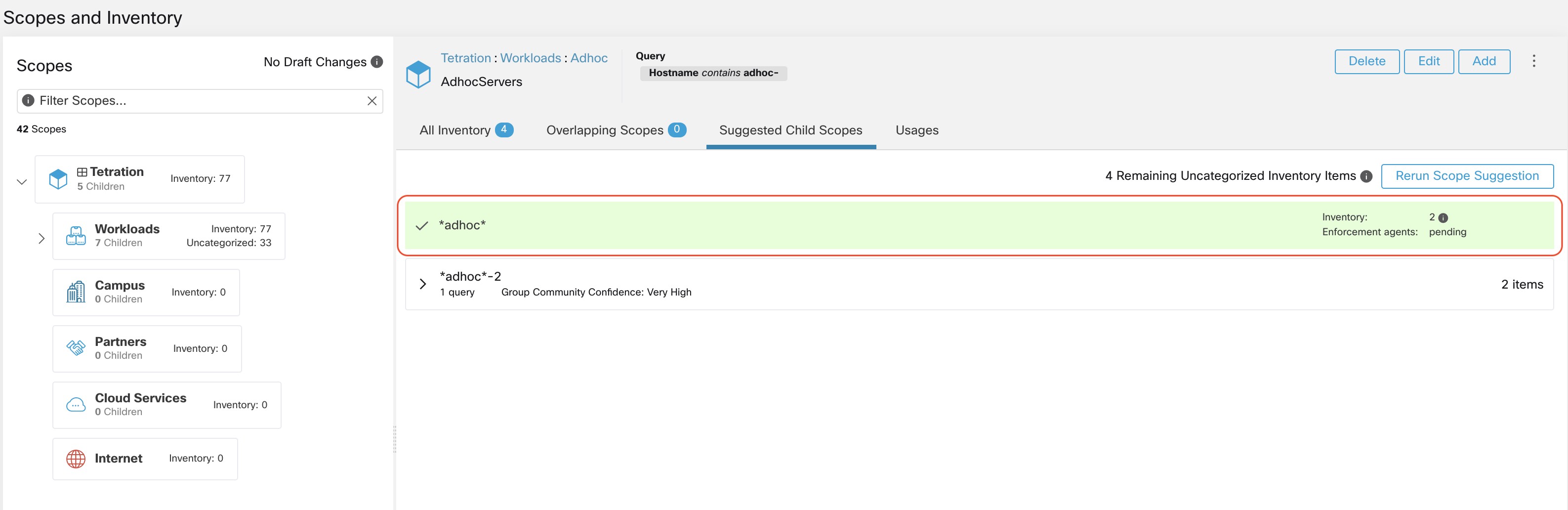
The user can repeat the process of scope creation from the remaining list of groups. The recommended workflow is to create one or more scopes and then re-run scope suggestion. A zero count for Uncategorized Inventory Items indicates that there is no inventory left to be further scoped (for the currently selected parent scope).
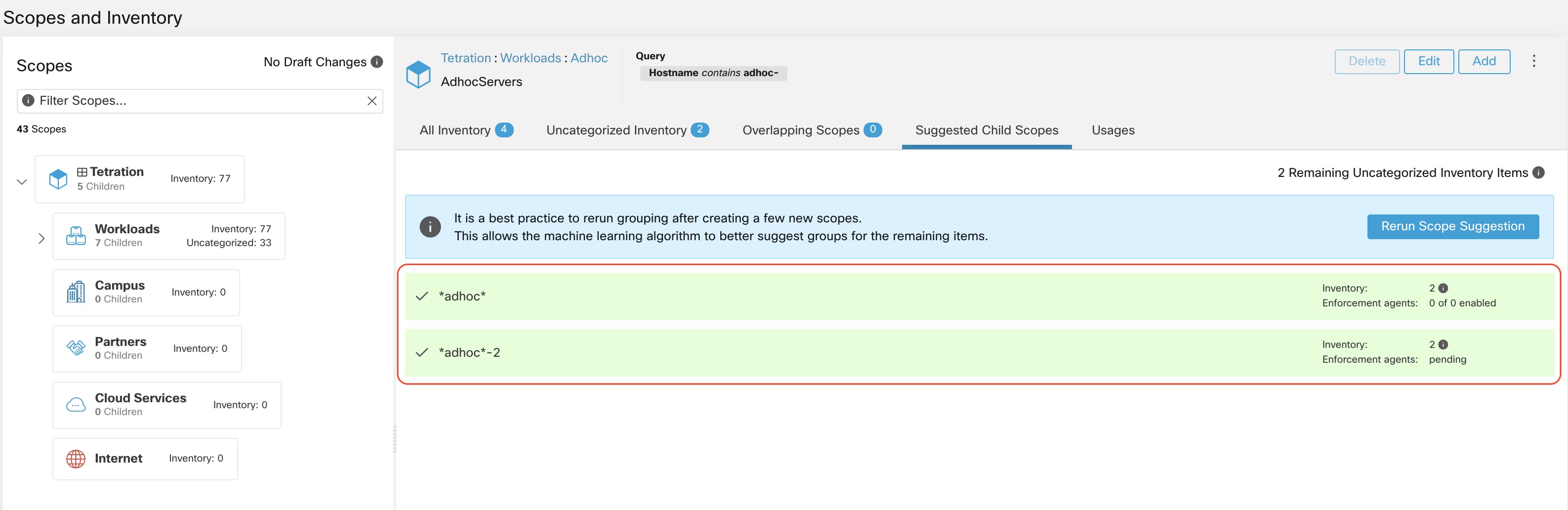
After the scope creation process is done (the uncategorized count is 0), user can repeat this process on the newly created child scopes in order to generate a deeper scope tree as desired.
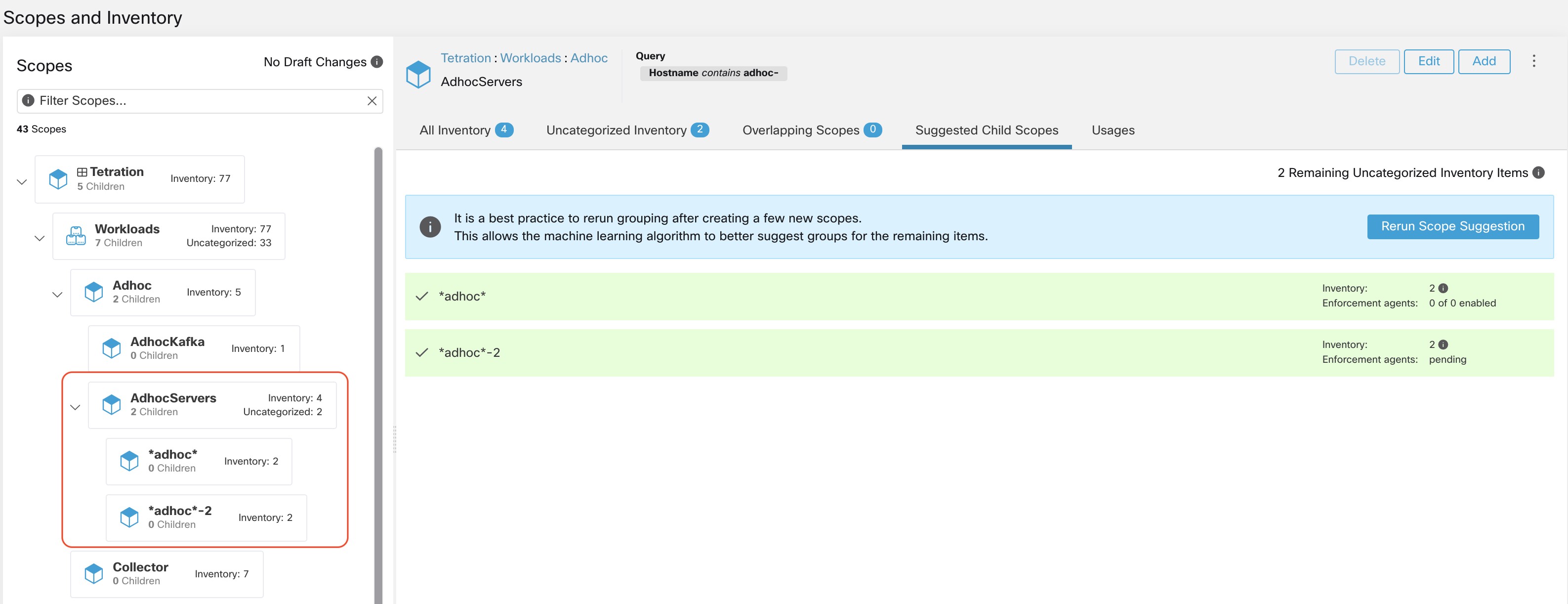
|
|
There is also a possibility that the uncategorized items in a scope do not partition well (e.g., do not form communities). In that case, the algorithm may return no groupings (an empty result). |
