Classification Examples
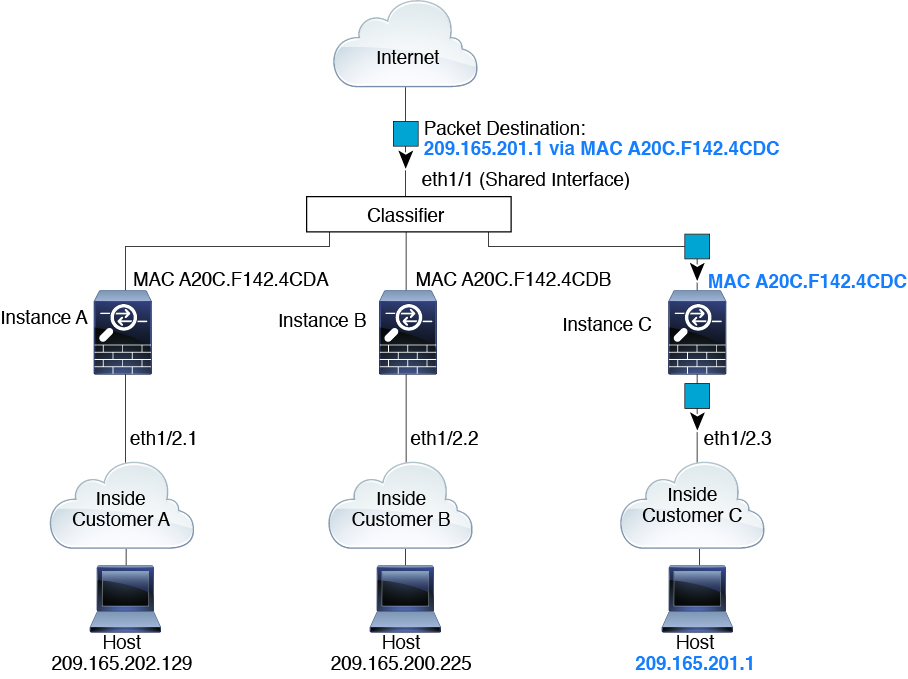
Packet Classification with a Shared Interface Using MAC Addresses
The following figure shows multiple instances sharing an outside interface. The classifier assigns the packet to Instance C because Instance C includes the MAC address to which the router sends the packet.
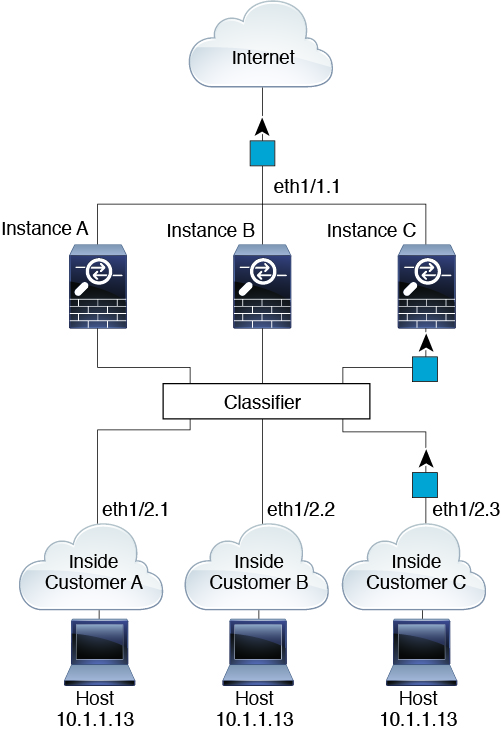
Incoming Traffic from Inside Networks
Note that all new incoming traffic must be classified, even from inside networks. The following figure shows a host on the Instance C inside network accessing the internet. The classifier assigns the packet to Instance C because the ingress interface is Ethernet 1/2.3, which is assigned to Instance C.
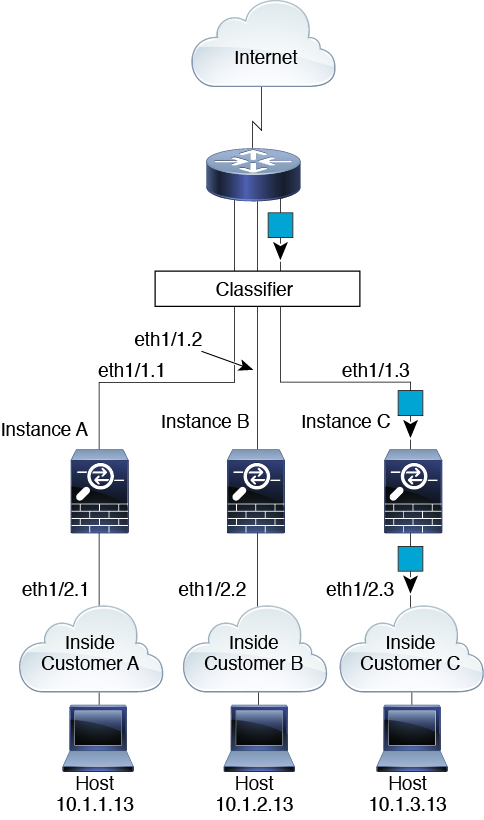
Transparent Firewall Instances
For transparent firewalls, you must use unique interfaces. The following figure shows a packet destined to a host on the Instance C inside network from the internet. The classifier assigns the packet to Instance C because the ingress interface is Ethernet 1/2.3, which is assigned to Instance C.
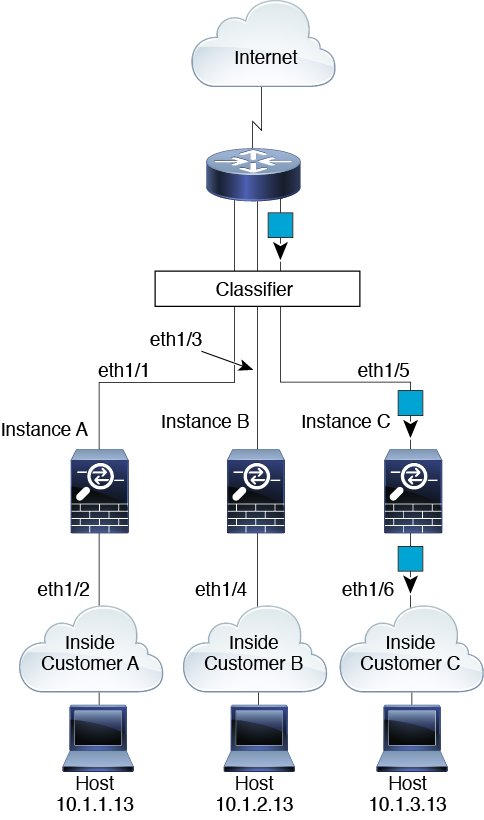
Inline Sets
For inline sets, you must use unique interfaces and they must be physical interfaces or EtherChannels. The following figure shows a packet destined to a host on the Instance C inside network from the internet. The classifier assigns the packet to Instance C because the ingress interface is Ethernet 1/5, which is assigned to Instance C.